As the idea of interconnected and intelligent manufacturing is gaining ground, competing in the world of Industry 4.0 can be challenging if you’re not on the very cusp of innovation.
Seeing the growing economic impact of IIoT around the globe, many professionals and investors have been asking themselves if the industry is on the verge of a technological revolution. But judging from the numbers and predictions, there is tangible and concrete evidence that the idea of smart manufacturing has already burst into corporate consciousness. According to IDC, global spending on the Internet of Things in 2020 is projected to top $840 billion if it maintains the 12.6% year-over-year compound annual growth rate. There is no doubt that a huge part of this expenditure will be devoted to the introduction of IoT into all types of industry, especially including manufacturing.
But there is not only the forecasts and statistics to tell us that the idea of Industrial Internet of Things is gaining traction across virtually all business sectors. Having already proven to be the crunch point in manufacturing, IIoT brings the reliability of the machine to machine communication, the security of preventive maintenance and the insight of big data analytics. In other words, the IIoT revolution has already begun.
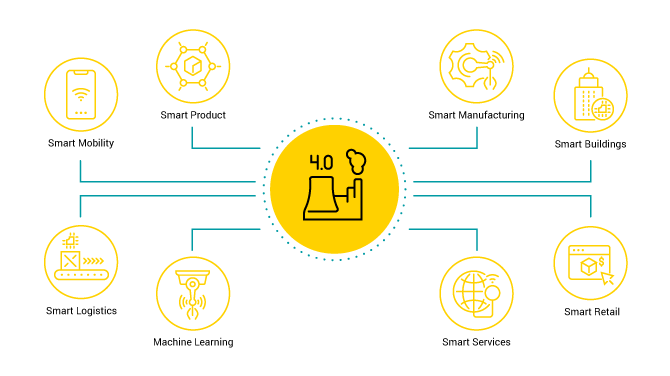
What is the Smart Factory?
Before we focus on the intricacies of the smart factory, by way of introduction, a few words must be said about its underlying concept, the Industrial Internet of Things. Though the idea has been around for quite a time now, it isn’t yet obvious to all what exactly it encompasses and what all its aspects are. Just as the regular Internet of Things aims to empower our everyday life by interconnecting devices and making them interact and cooperate to bring us easier and quicker solutions for our daily struggles (remember smart coffee makers?), the IIoT is the same concept, but applied to whole enterprises, like manufacturing, services or retail businesses. So, what we need to have to be talking about a real IIoT deployment, is not only machine-to-machine communication, but also bridging the gap between physical and digital assets within a factory and reducing man-to-machine cooperation by introducing smart automation and machine learning.
A Smart Factory is a concept deriving from IIoT that envisages a production environment as a fully automatized and intelligent network of systems that enables facilities, machines and logistics chains within the manufacturing plant to be managed without human intervention. Moreover, a smart factory is a place where all these things happen thanks to the exchange of data not only between production tools and machines, but also between all elements in the production technology chain. This in turn fuels machine learning so that operations can be carried out more efficiently and bring more savings than it would be ever possible if the production processes remained solely under human supervision.

What is the impact of the smart factory on enterprises?
There would be no hype nor double-digit growth estimates concerning the concept of Factory 4.0 if it weren’t for the benefits that the introduction of smart manufacturing processes can bring to any business. Creating a dynamic production environment thanks to the application of both automation and intelligence improves reliability, effectiveness and safety while reducing operation and downtime costs. Let’s have a closer look at how this is realized within the concept of a smart factory.
Production process monitoring
Whether it’s entirely manual or fully automated, every manufacturing process must be monitored in order to be controlled, effective and safe. Therefore, the efforts of the IoT projects in this industry sector have to concentrate on tracking the operations at all levels and gathering relevant data from machines or assets that would be otherwise only isolated pieces of gear with no ability to coordinate and control their own workflow.
But what the communication and interaction between the production tools brings to the process is more than just enhanced supervision and monitoring capabilities. Based on the smart factory production strategies, improvements can be introduced in real time, quickly leading to production cycle optimization. Moreover, the more automated and controllable a process is, the less it is prone to human errors, which not only increases productivity through reducing downtime or maintenance costs, but also improves final product quality.


 Share your Details for subscribe
Share your Details for subscribe